We use cookies to make your experience better. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our use of cookies. More information can be found in our Privacy Policy.
SSL
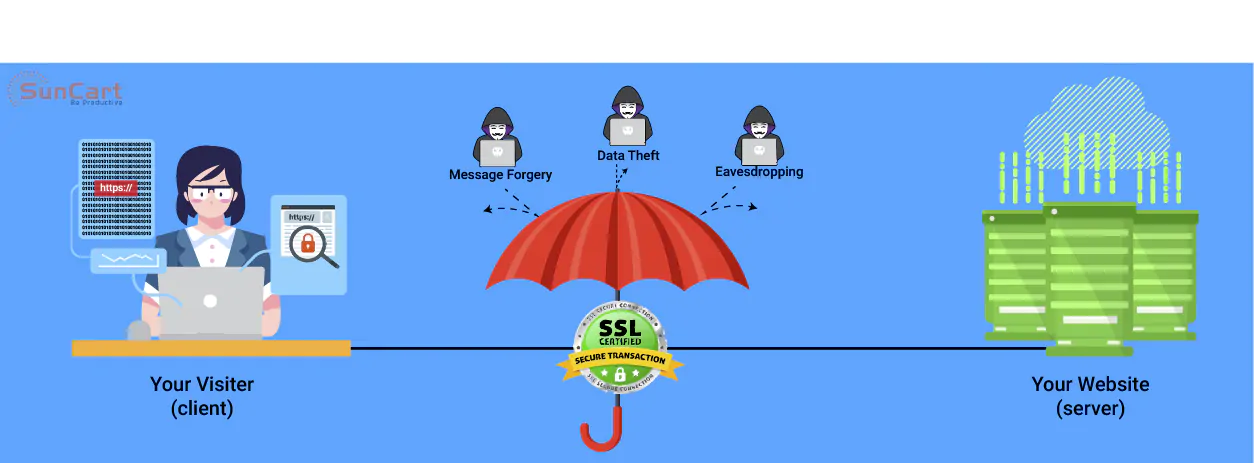
SSL Stands for "Secure Sockets Layer." SSL is a secure protocol developed for sending information securely over the Internet. Many websites use SSL for secure areas of their sites, such as user account pages and online checkout. Usually, when you are asked to "log in" on a website, the resulting page is secured by SSL.
While SSL is most commonly seen on the Web (HTTP), it is also used to secure other Internet protocols, such as SMTP for sending e-mail and NNTP for newsgroups. Early implementations of SSL were limited to 40-bit encryption, but now most SSL secured protocols use 128-bit encryption or higher.
How does SSL Works?
SSL consists of two distinct entities namely server and client. The client is the entity which starts the transactions on the other hand server is the entity which responds to client and negotiates with cipher suites and also does negotiate that which cipher suites will be used for encryption. In SSL client is Web browser and the server is the Website.
SSL works on three protocols namely the Handshake Protocol, the Record Protocol & the Alert Protocol. The server is authenticated by the client at the time of the Handshake Protocol. After that Record Protocol phase comes into play to encrypt the data transfer once the handshake protocol is completed. Lastly, Alert Protocol is used to handle any questionable packets if any alarms tick on any point during the time of the session.
SSL Handshake
In this protocol, the server is always authenticated by the client, and the server also consists of the option of authenticating the client. In other words, you can say during the Handshake Protocol clients are not authenticated by the Web servers as it has other ways to verify the client other than SSL.
At the time of Handshake Protocol, the above steps take place, firstly the session capabilities are negotiated means the encryption (ciphers) algorithms are negotiated & secondly server is authenticated to the client.
Symmetric cryptography is used for the bulk data encryption during the transfer phase in SSL and asymmetric cryptography (PKI) is used to negotiate the key used for the symmetric encryption. Sometimes, it’s possible that the server may ask the client to authenticate itself but it’s optional and not necessary to the protocol.
SSL Records
Record Protocol is responsible for handling all the encryption of the messaging. This protocol offers a common format to frame all the Alert, ChangeCipherSpec, Handshake & application protocol messages.
SSL records include encapsulated data, digital signature, message type, version & length. SSL records are 8 bytes long. One thing to note is that sometimes it’s possible that message sometimes may include padding and padding length in the frame as the record length is fixed.
SSL Alert Protocol
As we saw earlier, that Alert Protocol offers to handle any questionable packets. So, if the server or client detects any error, it sends an alert containing the error. Typically there are three types of alert message namely, warning, critical & fatal. Based on this alert message received, the session can be further restricted (warning or critical) or else terminated (fatal).
Benefits Of SSL:
The SSL protocol is the basic element to protect your customers from online threats
It protects all the sensitive data like the credit card details and other sensitive data shared between your website and external parties and keeps it confidential
With an SSL certificate on your website, you will know that the website is protected and it builds credibility with customers.
In Short!
Hackers are becoming more adventurous in compromising websites, especially in commercial sites where sensitive financial information is exchanged. Infringement can lead to greater liability costs and can shake customer trust in a business. This is the reason why all e-commerce sites should use secure socket layer (SSL) protection.
